
Formazione Cisco
Insoft Services è uno dei pochi fornitori di formazione in EMEAR a offrire una gamma completa di certificazione Cisco e formazione tecnologica specializzata.
Dettagli
Certificazioni Cisco
Sperimenta un approccio di apprendimento misto che combina il meglio della formazione con istruttore e dell'e-learning autogestito per aiutarti a prepararti per l'esame di certificazione.
Dettagli

Cisco Learning Credits
I Cisco Learning Credits (CLC) sono voucher di formazione prepagati riscattati direttamente con Cisco che semplificano la pianificazione del successo durante l'acquisto di prodotti e servizi Cisco.
Dettagli

Formazione Continua
The Cisco Continuing Education Program offers all active certification holders flexible options to recertify by completing a variety of eligible training items.
Dettagli

Cisco Digital Learning
Certified employees are VALUED assets. Explore Cisco official Digital Learning Library to educate yourself through recorded sessions.
Dettagli

Cisco Business Enablement
The Cisco Business Enablement Partner Program focuses on sharpening the business skills of Cisco Channel Partners and customers.
Dettagli
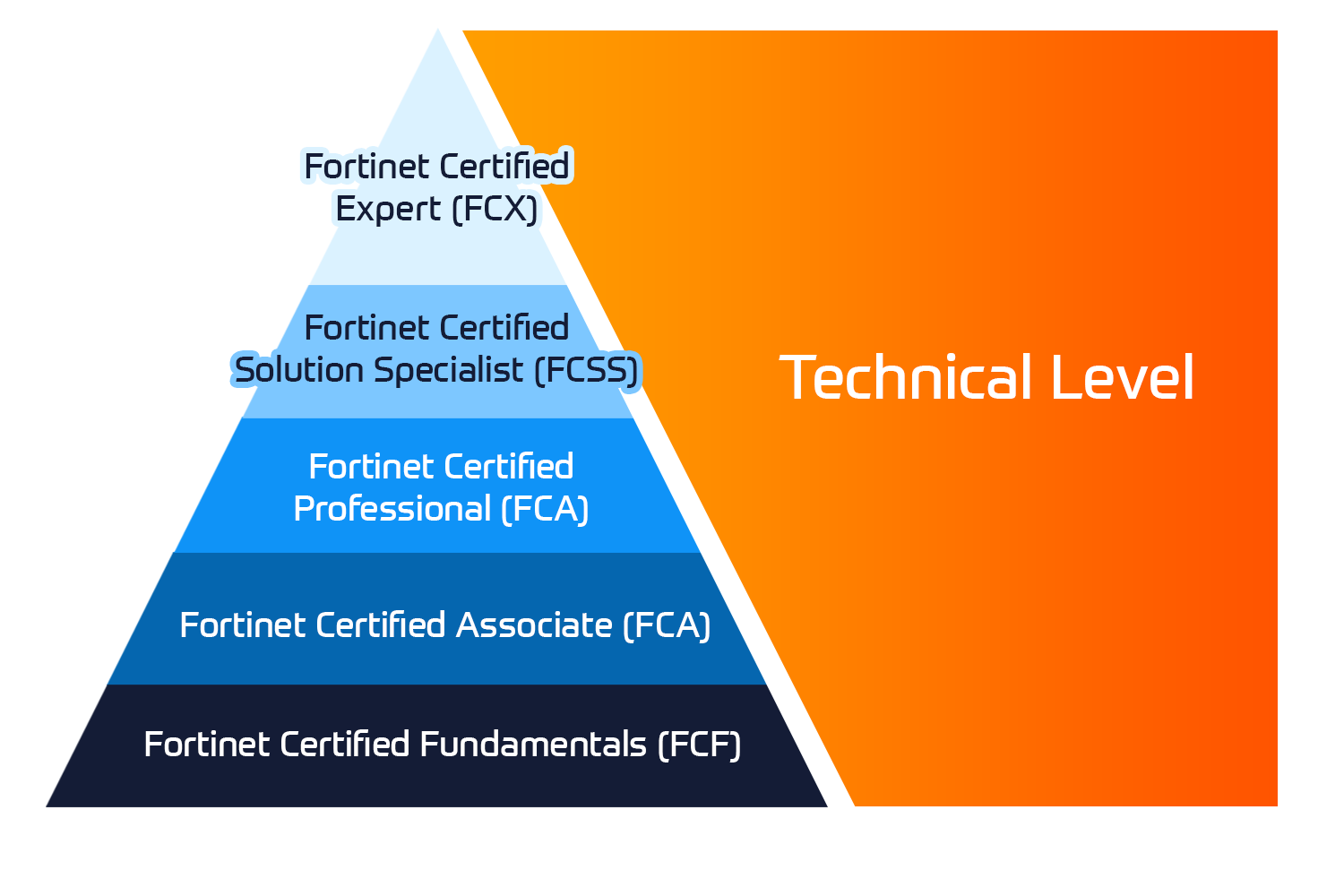
Certificazioni Fortinet
Il programma Fortinet Network Security Expert (NSE) è un programma di formazione e certificazione di otto livelli per insegnare agli ingegneri la sicurezza della loro rete per le competenze e l'esperienza di Fortinet FW.
Dettagli

Corsi di formazione tecnica
Insoft è riconosciuto come Fortinet Authorized Training Center in sedi selezionate in tutta l'EMEA.
Corsi tecnici

Catalogo Fortinet
Esplora un'ampia varietà di programmi Fortinet in diversi paesi e corsi online.
Dettagli
Fortinet Servizi Professionale
Il team riconosciuto a livello globale di esperti certificati ti aiuta a fare una transizione più fluida con i nostri pacchetti di consulenza, installazione e migrazione predefiniti per una vasta gamma di prodotti Fortinet.
Dettagli

Catalogo Microsoft
Insoft Services fornisce formazione Microsoft in EMEAR. Offriamo corsi di formazione tecnica e certificazione Microsoft guidati da istruttori di livello mondiale.
Corsi tecnici

Corsi di formazione
Impara conoscenze e abilità eccezionali di Extreme Networks.Find all the Extreme Networks online and instructor led class room based calendar here.
Corsi tecnici

Certificazioni Extreme
Forniamo un curriculum completo di competenze tecniche sul conseguimento della certificazione.
Dettagli

Accreditamento ATP
In qualità di partner di formazione autorizzato (ATP), Insoft Services garantisce che tu riceva i più alti standard di istruzione disponibili.
Dettagli

Pacchetti di consulenza
Forniamo un supporto innovativo e avanzato per la progettazione, l'implementazione e l'ottimizzazione delle soluzioni IT.La nostra base di clienti comprende alcune delle più grandi telco a livello globale.
Soluzioni & Servizi

Chi siamo
Insoft fornisce servizi di formazione e consulenza autorizzati per fornitori IP selezionati.Scopri come stiamo rivoluzionando il settore.
Dettagli
Contact Us
We would love to hear from you. Please complete this form to pre-book or request further information about our delivery options.


 United Kingdom
United Kingdom Germany
Germany Denmark
Denmark Norway
Norway Sweden
Sweden Netherlands
Netherlands Finland
Finland











 Duration
Duration
 Delivery
Delivery  Price
Price