Cisco træning
Insoft Services er en af de få uddannelsesudbydere i EMEAR, der tilbyder hele spektret af Cisco-certificering og specialiseret teknologiuddannelse.
Lær hvordan
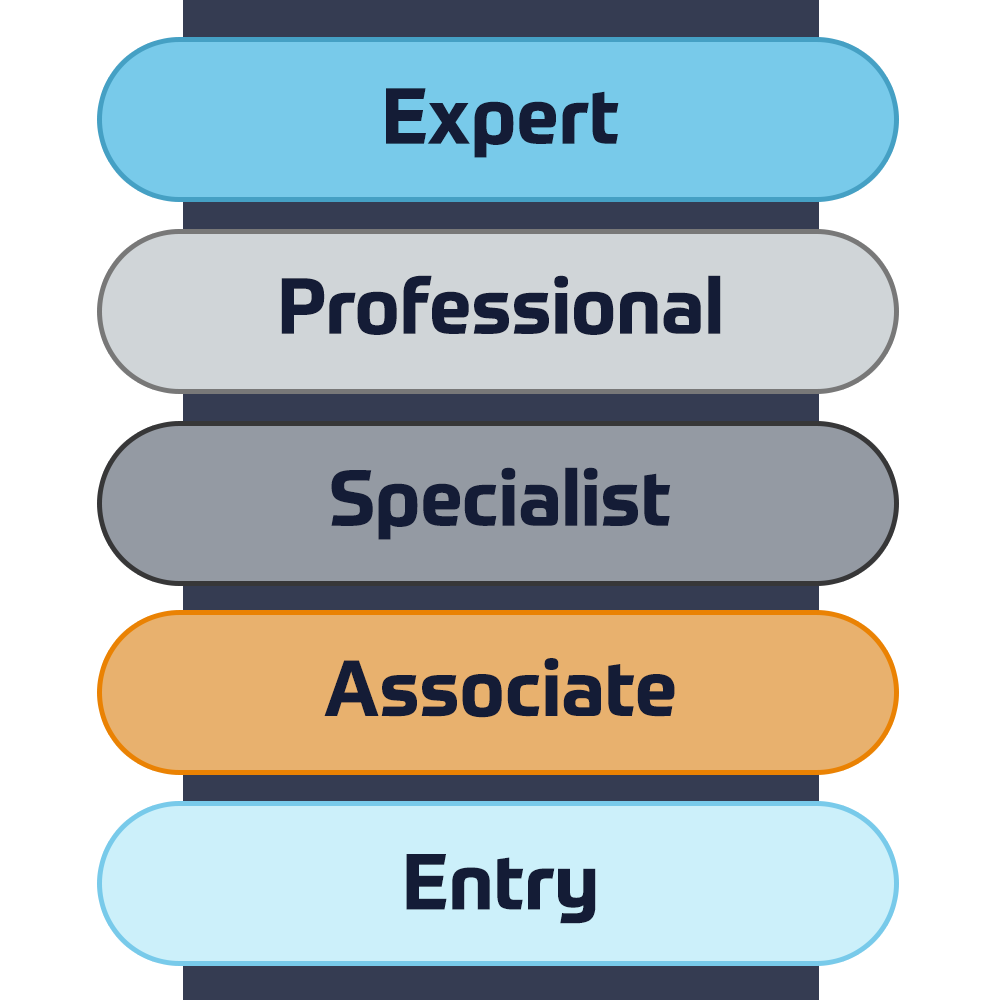
Cisco-certificeringer
Oplev en blandet læringsmetode, der kombinerer det bedste fra instruktørstyret træning og e-læring i eget tempo for at hjælpe dig med at forberede dig til din certificeringseksamen.
Lær hvordan

Cisco Learning Credits
Cisco Learning Credits (CLCs) er forudbetalte træningskuponer, der indløses direkte med Cisco, og som gør det nemmere at planlægge din succes, når du køber Cisco-produkter og -tjenester.
Lær hvordan

Cisco Efteruddannelse
Cisco Continuing Education Program tilbyder alle aktive certificeringsindehavere fleksible muligheder for at gencertificere ved at gennemføre en række kvalificerede træningselementer.
Lær hvordan

Cisco Digital Learning
Certificerede medarbejdere er VÆRDSATTE aktiver. Udforsk Ciscos officielle digitale læringsbibliotek for at uddanne dig selv gennem optagede sessioner.
Lær hvordan

Cisco Business Enablement
Cisco Business Enablement Partner Program fokuserer på at skærpe Cisco Channel Partners og kunders forretningsmæssige færdigheder.
Lær hvordan
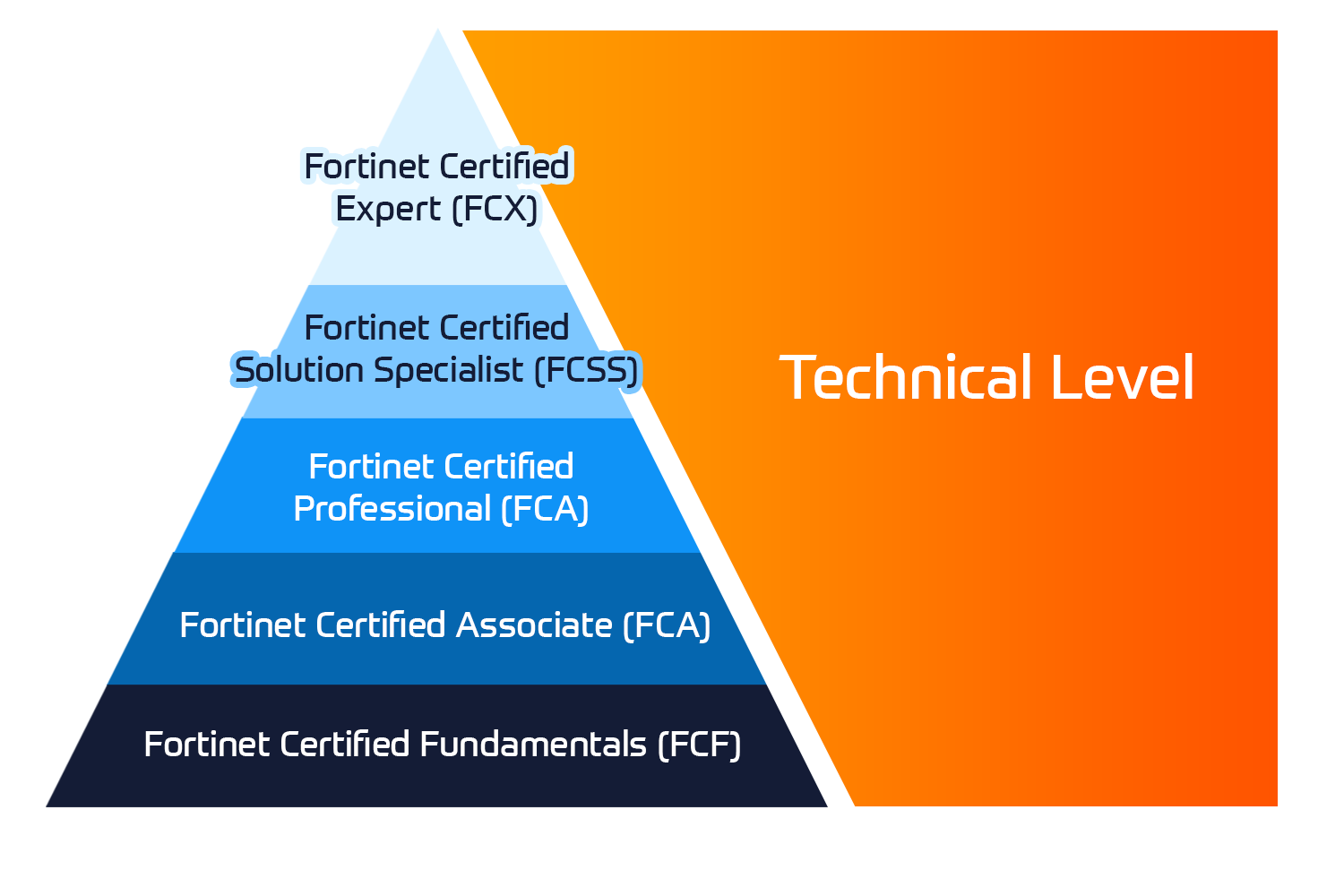
Fortinet-certificeringer
Fortinet Network Security Expert (NSE) -programmet er et otte-niveau uddannelses- og certificeringsprogram for at undervise ingeniører i deres netværkssikkerhed for Fortinet FW-færdigheder og erfaring.
Lær hvordan

Fortinet træning
Insoft er anerkendt som Autoriseret Fortinet Training Center på udvalgte steder på tværs af EMEA.
Tekniske kurser

Fortinet kursuskatalog
Udforsk hele Fortinet-træningskataloget. Programmet omfatter en bred vifte af selvstændige og instruktørledede kurser.
Lær hvordan
Fortinet Professionelle Services
Globalt anerkendte team af certificerede eksperter hjælper dig med at gøre en mere jævn overgang med vores foruddefinerede konsulent-, installations- og migreringspakker til en lang række Fortinet-produkter.
Lær hvordan

AWS træning
Træningen inkluderer laboratorier i eget tempo til praktisk AWS-øvelse i virkelige scenarier, så du kan lære i dit eget tempo, i klassen, på arbejdet eller online.
Tekniske kurser

Extreme træning
Find all the Extreme Networks online and instructor led class room based calendar here.
Tekniske kurser

Tekniske certificeringer
Vi leverer omfattende læseplan for tekniske kompetencefærdigheder på certificeringspræstationen.
Lær hvordan

ATP-akkreditering
Som autoriseret uddannelsespartner (ATP) sikrer Insoft Services, at du får de højeste uddannelsesstandarder, der findes.
Lær hvordan

Løsninger og tjenester
Vi leverer innovativ og avanceret support til design, implementering og optimering af IT-løsninger. Vores kundebase omfatter nogle af de største Telcos globalt.
Lær hvordan

Om os
Insoft tilbyder autoriseret uddannelses- og konsulentbistand til udvalgte IP-leverandører. Få mere at vide om, hvordan vi revolutionerer branchen.
Lær hvordan
Contact Us
We would love to hear from you. Please complete this form to pre-book or request further information about our delivery options.


 United Kingdom
United Kingdom Germany
Germany Norway
Norway Sweden
Sweden Italy
Italy Netherlands
Netherlands Finland
Finland










